Back to Course
Electrocardiology
0% Complete
0/0 Steps
-
Basics of ECG Interpretation11 Topics
-
Normal ECG Parameters
-
ECG Interpretation of Chamber Enlargement4 Topics
-
Dysrhythmias
-
Bradycardia
-
Heart Block3 Topics
-
Sick Sinus Syndrome
-
Tachycardia8 Topics
-
Hyperkalemia
-
Myocardial Hypoxia/Ischemia
-
Low Amplitude QRS Complex
-
Wide QRS Complex
-
Bundle Branch Block
-
Differentials for ECG Abnormalities
Lesson 1,
Topic 5
In Progress
Direction of ECG wave
Lesson Progress
0% Complete
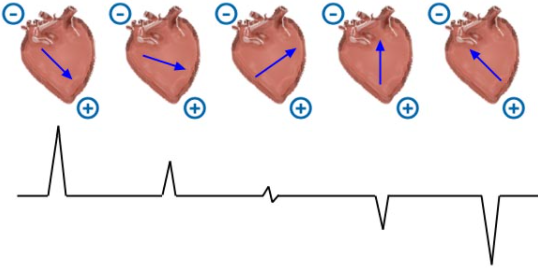
An ECG lead utilizes a combination of electrodes (attached to the patient) to provide a unique perspective of the electrical activity travelling through the heart. Each lead has a positive pole and a negative pole, and the difference in electrical potential between these poles is graphed over time. As a wave of electrical depolarization moves parallel to the direction of a lead, if it moves towards the positive pole of the lead, a positive deflection occurs on the ECG. If it moves toward the negative pole of the lead, a negative deflection occurs on the ECG.
