Back to Course
Electrocardiology
0% Complete
0/0 Steps
-
Basics of ECG Interpretation11 Topics
-
Normal ECG Parameters
-
ECG Interpretation of Chamber Enlargement4 Topics
-
Dysrhythmias
-
Bradycardia
-
Heart Block3 Topics
-
Sick Sinus Syndrome
-
Tachycardia8 Topics
-
Hyperkalemia
-
Myocardial Hypoxia/Ischemia
-
Low Amplitude QRS Complex
-
Wide QRS Complex
-
Bundle Branch Block
-
Differentials for ECG Abnormalities
Lesson 1,
Topic 6
In Progress
Frontal Plane Leads
Lesson Progress
0% Complete
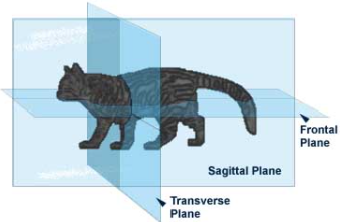
The frontal, sagittal, and transverse (also called horizontal) planes are illustrated in the cat above. Leads I, II, III, aVR, aVL, and aVF are the leads available in the frontal plane.
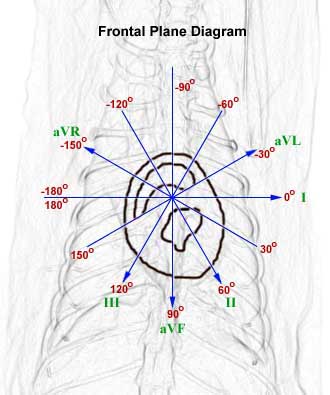
In the illustration above, a cross-section of the heart is superimposed on the frontal plane diagram. The arrow heads point toward the positive pole of each lead.
The frontal plane diagram shows the relationship of the 6 leads in the frontal plane. This diagram includes the angles in the frontal plane and the direction of each lead with its negative and positive pole.
The frontal plane corresponds to the radiographic V/D or D/V view of the heart.