Back to Course
Electrocardiology
0% Complete
0/0 Steps
-
Basics of ECG Interpretation11 Topics
-
Normal ECG Parameters
-
ECG Interpretation of Chamber Enlargement4 Topics
-
Dysrhythmias
-
Bradycardia
-
Heart Block3 Topics
-
Sick Sinus Syndrome
-
Tachycardia8 Topics
-
Hyperkalemia
-
Myocardial Hypoxia/Ischemia
-
Low Amplitude QRS Complex
-
Wide QRS Complex
-
Bundle Branch Block
-
Differentials for ECG Abnormalities
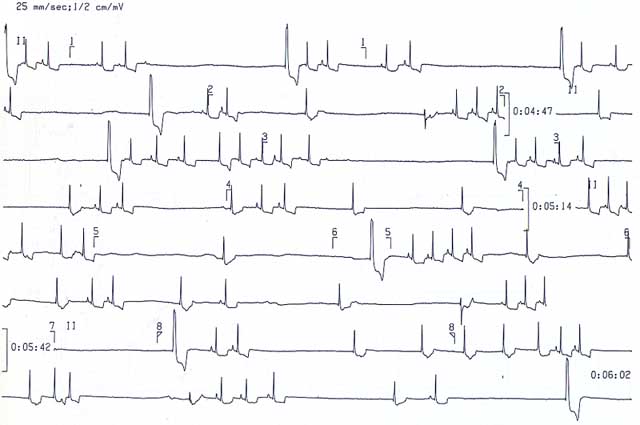
Sick Sinus Syndrome refers to a group of disorders involving the sino-atrial node usually with further involvement of the atrio-ventricular node, His bundle and/or bundle branches. Frequently, multiple areas of the conduction system are involved.
ECG findings (may include any of the following):
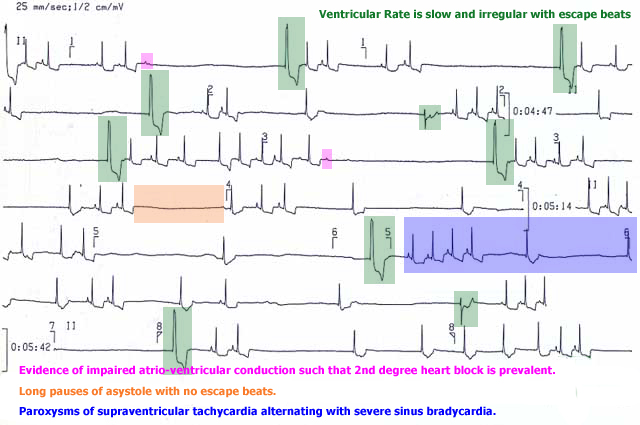
- A slow and irregular atrial rate (impaired sino-atrial activity), severe sinus bradycardia, or long pauses of asystole with no escape beats
- Evidence of impaired atrio-ventricular conduction such as 2nd degree heart block
- The ventricular rate is slow and irregular.
- Ventricular escape beats are common, though they are often slow to manifest (follow a longer pause than usual)
- Paroxysms of supraventricular tachycardia alternating with severe sinus bradycardia
Etiology:
- May have SA nodal artery disease – ischemia
- Fibrosis of SA node with partial involvement of the rest of conduction system
- Possibly inherited in some breeds as Miniature Schnauzer, West Highland White terrier
- Usually idiopathic
Consequences:
- Periods of asystole are associated with syncope, pre-syncope, weakness
- The paroxysms of supraventricular tachycardia may also cause clinical signs
Treatment:
- Atropine is usually not effective (or at least there is a suboptimal atropine response), though some anticholinergics or sympathomimetics may accelerate the ventricular rate and provide a temporary response
- Permanent pacemaker implantation is the only definitive therapy
