Back to Course
Electrocardiology
0% Complete
0/0 Steps
-
Basics of ECG Interpretation11 Topics
-
Normal ECG Parameters
-
ECG Interpretation of Chamber Enlargement4 Topics
-
Dysrhythmias
-
Bradycardia
-
Heart Block3 Topics
-
Sick Sinus Syndrome
-
Tachycardia8 Topics
-
Hyperkalemia
-
Myocardial Hypoxia/Ischemia
-
Low Amplitude QRS Complex
-
Wide QRS Complex
-
Bundle Branch Block
-
Differentials for ECG Abnormalities
Lesson 8,
Topic 3
In Progress
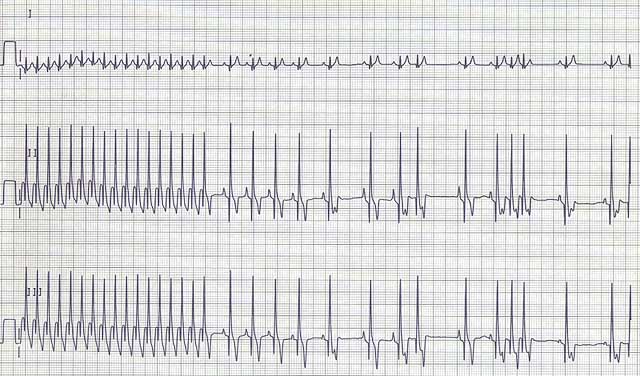
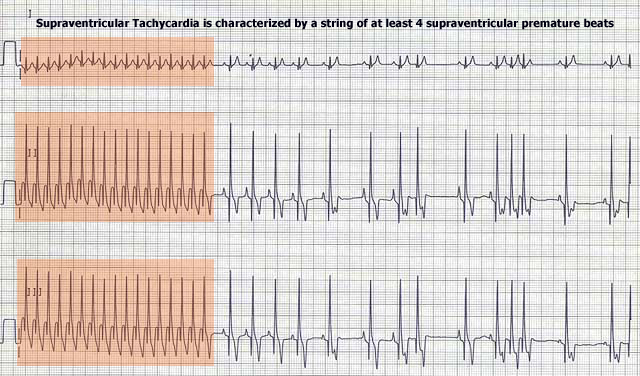
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Lesson Progress
0% Complete
ECG Findings:
- A run of at least 4 supraventricular premature beats in a row (see above).
- Often occurs as paroxysms (bursts).
Etiology: The same as for supraventricular premature beats (see above)
Consequences: Paroxysms of supraventricular tachycardia can result in weakness, syncope, and heart failure when sustained and untreated
Treatment:
- Efforts to increase the parasympathetic tone and thereby reduce A-V nodal conduction may be useful in slowing the ventricular response, assisting in detecting atrial activity (P waves on ECG), and differentiating supraventricular tachycardia from ventricular tachycardia. This may be accomplished by:
- Vagal maneuvers such as ocular pressure or carotid sinus massage
- Reflex induced increase in vagal tone using phenylephrine
- Anti-arrhythmics including beta blockers (e.g. propranolol, metoprolol, atenolol), calcium channel blockers (diltiazem), sotalol, or digoxin.
