Back to Course
Electrocardiology
0% Complete
0/0 Steps
-
Basics of ECG Interpretation11 Topics
-
Normal ECG Parameters
-
ECG Interpretation of Chamber Enlargement4 Topics
-
Dysrhythmias
-
Bradycardia
-
Heart Block3 Topics
-
Sick Sinus Syndrome
-
Tachycardia8 Topics
-
Hyperkalemia
-
Myocardial Hypoxia/Ischemia
-
Low Amplitude QRS Complex
-
Wide QRS Complex
-
Bundle Branch Block
-
Differentials for ECG Abnormalities
Lesson 8,
Topic 1
In Progress
Sinus Tachycardia
Lesson Progress
0% Complete
Sinus tachycardia is a sinus rhythm with an increased sinus nodal rate, and therefore ventricular rate.
- Dog (<20 kg) with heart rate >180 bpm
- Dog (>20 kg) with heart rate >160 bpm
- Cat with heart rate >240 bpm
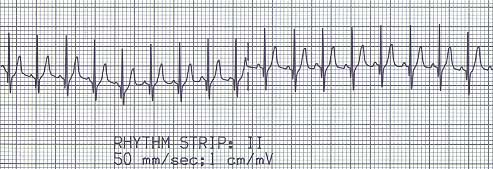
Examples of etiologies include:
- Pain
- Fever
- Anemia
- Hypovolemia
- Reduced cardiac output (and resultant hypotension)
- Hyperthyroidism
- Excitement or stress
Consequences:
- If HR is excessive, cardiac output may fall due to reduced diastolic filling time
- Coronary perfusion decreases, also due to shorter diastole
- Increased myocardial oxygen consumption per beat
- The above are generally only significant if sustained for long period of time
Treatment: Treat the underlying cause.
